
Unpacking Systematic Review Research: Innovative Teaching Strategies for Advanced Nursing Instructors
Mastering the ability to conduct systematic reviews is essential for ensuring that healthcare practices are based on the most reliable evidence. For educators, the challenge lies in making this complex methodology both accessible and engaging. How can instructors effectively bring the process of systematic reviews to life? Here are some strategies to enhance your teaching methods.
1. Interactive Workshops
Gone are the days of one-way lectures! Transform your classroom into a workshop where students can actively participate in the systematic review process. Utilize small group exercises that revolve around formulating research questions, developing inclusion criteria, and practicing data extraction. Interactive sessions not only enhance understanding but also keep students motivated.
2. Real-World Case Studies
Nothing beats learning from the real world. Use actual case studies from clinical settings to illustrate the impact of systematic reviews on patient outcomes and policy-making. Encourage students to critique these studies, examine the methodologies used, and discuss potential pitfalls. This approach not only refines critical thinking skills but also highlights the real-world relevance of systematic reviews.
3. Incorporate Technology
Leverage technology to make systematic review research more accessible and interactive. Introduce students to software tools like Covidence or Rayyan, which facilitate managing and executing systematic reviews. Hosting virtual discussions or webinars with experts in the field can also provide students with diverse perspectives and insights.
4. Collaborative Projects
Encourage a collaborative learning environment by assigning group projects that mimic the systematic review process. Students can work together to select a topic, conduct literature searches, and synthesize findings. Collaboration not only mirrors the teamwork often required in professional settings but also allows students to learn from one another's strengths and perspectives.
5. Flipped Classroom Approach
Consider flipping the classroom to maximize interactive learning. Assign pre-class readings or recorded lectures on the basics of systematic reviews, then use class time for discussions, workshops, or practical exercises. This model nurtures independent learning while reinforcing concepts through hands-on application.
6. Critical Appraisal Skills
Systematic reviews are all about assessing quality and bias. Equip your students with the tools to critically appraise research by providing them with checklists or appraisal frameworks, such as the CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Program) tools. Engaging students in debates or peer-review exercises can further sharpen their analytical skills.
7. Guest Lectures and Networking
Invite seasoned researchers or practitioners to share their experiences and insights on conducting systematic reviews. Their stories can provide invaluable lessons and inspire students. Additionally, networking opportunities can open doors for mentorship or collaboration in future research endeavors.
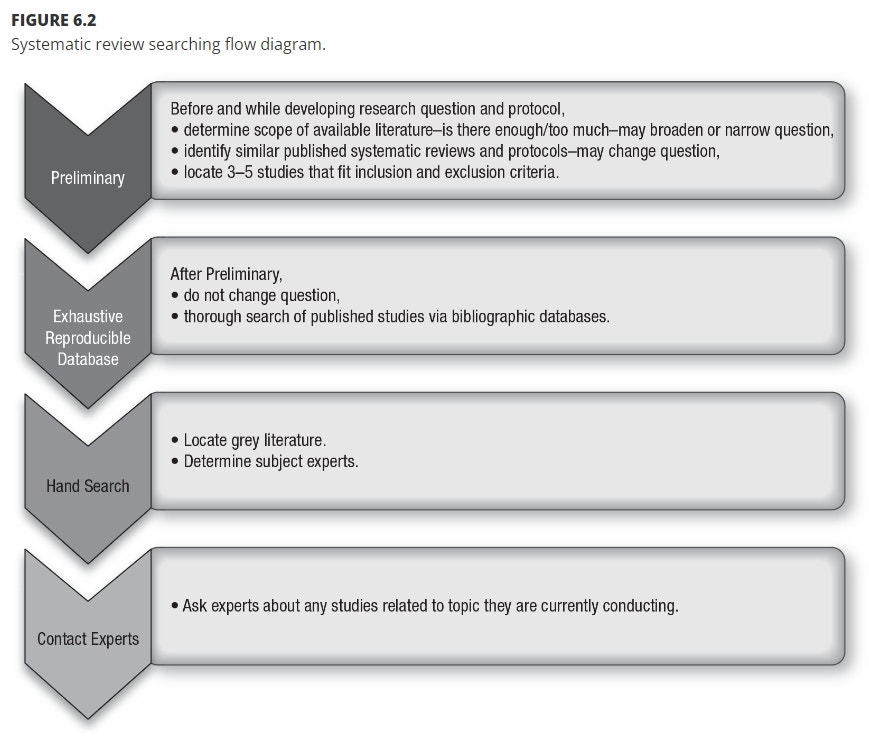
To enhance your students' understanding of systematic review research, Comprehensive Systematic Review for Advanced Practice Nursing, provides a visual representation of the process. It outlines at least four types of searches involved in a systematic review project: preliminary, exhaustive database, hand search, and expert consultation.

Teaching systematic review research in advanced nursing can be a daunting task, but with a blend of interactive, real-world, and technology-enhanced strategies, instructors can make this essential skill both accessible and intriguing. By fostering an environment of collaboration and critical thinking, educators will not only prepare their students for successful careers but also contribute to the advancement of evidence-based practice in healthcare. So, why not spark a little curiosity and innovation in your classroom today?
Comprehensive Systematic Review for Advanced Practice Nursing, focus on the search process and evidence quality, this text outlines the knowledge and skills needed to conduct a Comprehensive Systematic Review (CSR) in eight steps. It guides readers in writing a CSR proposal, final report, and policy brief based on findings. Two completed proposals and systematic reviews illustrate the entire process. Additionally, the text covers research software and provides strategies for effective information searching.

