
Teaching the Evidence-Based Practice Improvement Model: An Example Scenario
Incorporating the Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) Improvement Model into your nursing course can be transformative for students. One effective way to teach this model is through realistic scenarios that allow students to apply their knowledge and skills in a practical setting. Here’s an example scenario that can be used in the classroom.
Scenario: Improving Diabetes Management in a Hospital Setting
Objective: To enhance students' understanding of the EBP Improvement Model by addressing a common clinical issue—diabetes management.
Background: A local hospital has noticed a high rate of readmissions among diabetic patients. Data indicates that many patients are struggling with self-management post-discharge, leading to complications and hospital returns. The hospital administration wants to implement a new evidence-based approach to improve patient outcomes.
Step 1: Assign Roles
Divide the class into groups and assign each student a specific role related to the scenario. Roles may include:
-
Nurse: Responsible for patient education and monitoring.
-
Patient: A diabetic individual managing their condition.
-
Healthcare Administrator: Oversees policy implementation and resource allocation.
-
Endocrinologist: Provides expertise on diabetes management and treatment options.
Step 2: Present the Scenario
Introduce the scenario to the class, providing background information and data about the readmission rates. Explain that the students must work together to develop an evidence-based intervention aimed at improving diabetes management for patients post-discharge.
Step 3: Research and Discussion
Give the groups time to research current evidence-based practices related to diabetes education and management. Encourage them to explore topics such as:
-
Best practices for patient education
-
Effective communication strategies
-
Technology use in monitoring and supporting patients
As groups discuss their findings, they should consider how these practices could be implemented in the hospital setting.
Step 4: Develop an EBP Plan
Each group will then create an EBP improvement plan that includes:
-
Identification of the Problem: Outline the issues related to diabetes management and readmission.
-
Literature Review: Summarize the evidence found during research, highlighting effective interventions.
-
Implementation Strategy: Describe how they would implement their proposed solution, including training for staff and educational resources for patients.
-
Evaluation Metrics: Identify how they would measure the success of their intervention, such as decreased readmission rates or improved patient satisfaction scores.
Step 5: Present and Reflect
Have each group present their EBP improvement plan to the class. This not only reinforces their learning but also allows for constructive feedback from peers and the instructor.After presentations, hold a reflective discussion where students can share what they learned, the challenges they faced, and how they might apply these skills in their future practice.
According to Evidence-Based Practice Improvement, users of the original EBPI Model has led to sustained improvements, demonstrating its effectiveness in guiding enhancements. The new EBPI+ Model (see below) builds on lessons learned from the original's application in clinical settings, incorporating feedback from colleagues and students. This integration of academic and clinical insights resulted in a model that is both simple and user-friendly for practitioners.
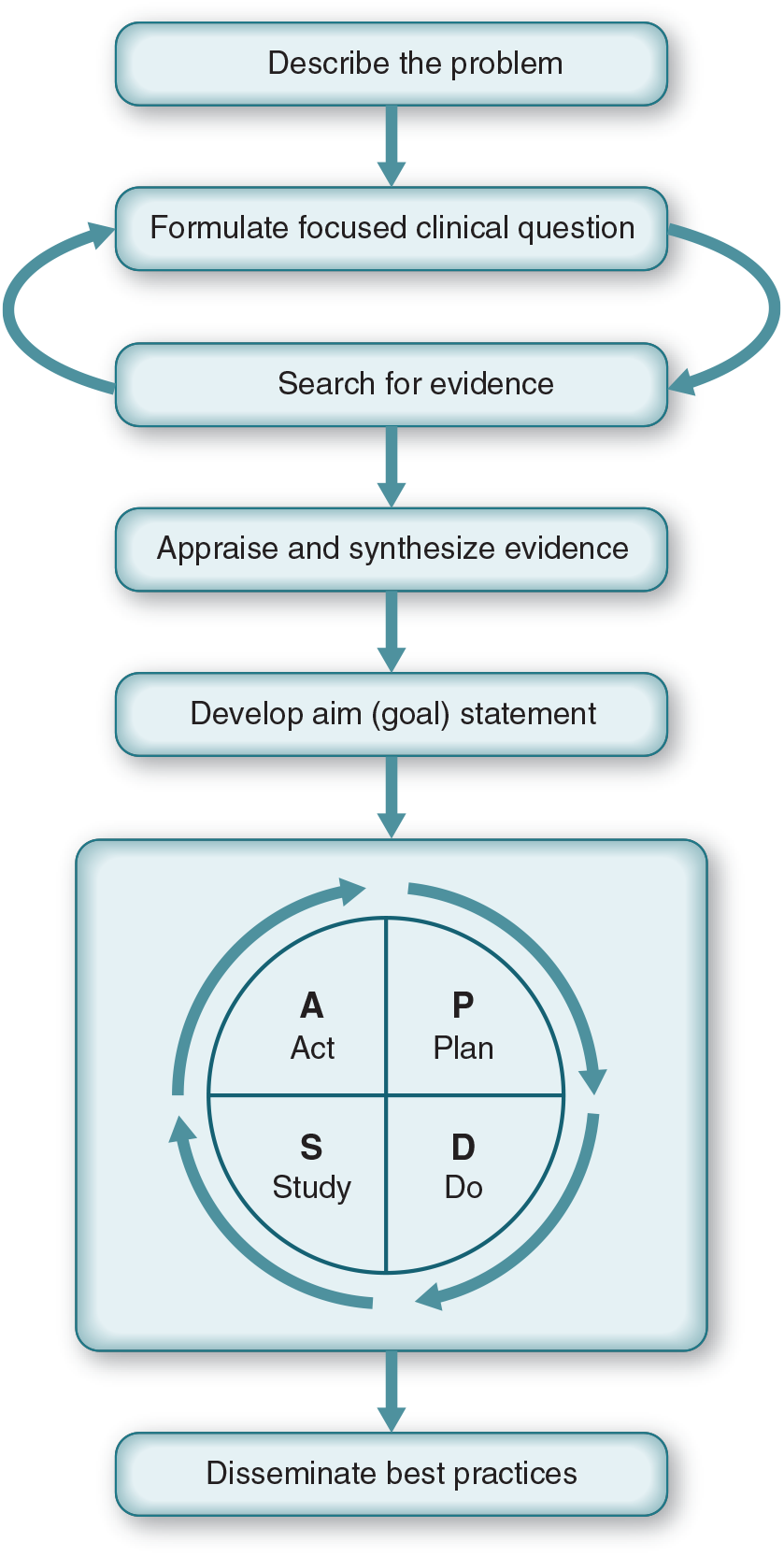

Using realistic scenarios like the diabetes management case in your nursing course can significantly enhance understanding of the Evidence-Based Practice Improvement Model. By engaging students in active problem-solving and collaboration, you prepare them to implement EBP effectively in their future careers, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes. Embrace the power of scenario-based learning, and watch your students thrive!
Evidence-Based Practice Improvement, text offers the academic and clinical healthcare communities a proven, practical model (EBPI+) for guiding evidence-based practice improvement projects. It emphasizes identifying and engaging project stakeholders while providing tools for effective decision-making.

