
Teaching Strategies for Common Challenges with the Pediatric Assessment Triangle
When teaching students about the Pediatric Assessment Triangle (PAT), it's important to anticipate common questions and areas of difficulty that might arise. Here are some of those questions and difficulties, along with strategies for addressing them:
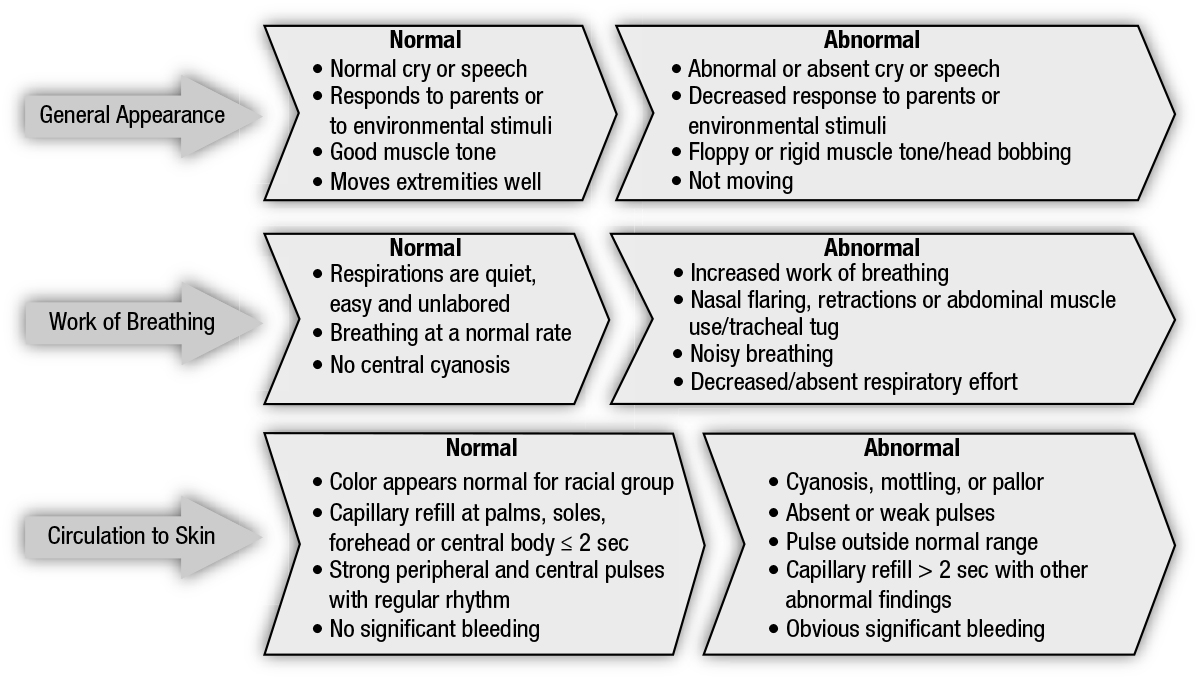
1. Understanding and Identifying Normal vs. Abnormal Findings
Difficulty: Students may struggle to distinguish between what is normal and what indicates a problem.
Strategy: Provide clear examples and case studies to highlight normal versus abnormal findings. Use visual aids and simulation to practice identifying these signs.
2. Interpreting Subtle Signs of Distress
Difficulty: Recognizing subtle signs of respiratory or circulatory distress can be challenging.
Strategy: Use practice scenarios and role-playing to help students become more adept at recognizing these subtle signs. Offer feedback on their assessments and encourage discussion about what to look for.
- Appearance: Look for signs of altered mental status such as lethargy, irritability, or unresponsiveness.
- Work of Breathing: Assess for signs of respiratory distress, such as nasal flaring, grunting, retractions, or abnormal breathing patterns.
- Circulation to the Skin: Observe skin color and temperature to detect signs of poor perfusion like pallor, cyanosis, or mottling.
3. Applying the PAT in Real-Life Situations
Difficulty: Students may find it hard to apply the PAT effectively in high-pressure or real-life situations.
Strategy: Incorporate simulation exercises that mimic real-life scenarios. Encourage students to practice PAT assessments in controlled environments to build confidence.
4. Prioritizing Interventions Based on PAT Findings
Difficulty: Deciding which interventions to prioritize based on PAT findings can be complex.
Strategy: Teach students how to prioritize based on severity and urgency. Use case studies to demonstrate how to make decisions about intervention priorities.
5. Communicating Findings to Caregivers
Difficulty: Effectively communicating PAT findings to caregivers, especially under stress, can be challenging.
Strategy: Practice communication skills through role-playing exercises where students explain their findings and action plans to simulated caregivers. Emphasize clear, empathetic, and informative communication.

By preparing for these questions and difficulties, you can better equip your students to master the Pediatric Assessment Triangle and apply it effectively in clinical settings.
Get your student nurses ready to deliver exceptional care to children of all ages with our extensive range of resources designed for pediatric nursing success.
Explore pediatric emergency procedures, medications, and a detailed look at the Pediatric Assessment Triangle (PAT) with quick access in the Rapid Access Guide for Pediatric Emergencies.
Discover the AACN Core Curriculum for Pediatric High Acuity, Progressive, and Critical Care, Third Edition, featuring pediatric critical care, high acuity courses, and essential AACN guidelines for superior nursing practice.


